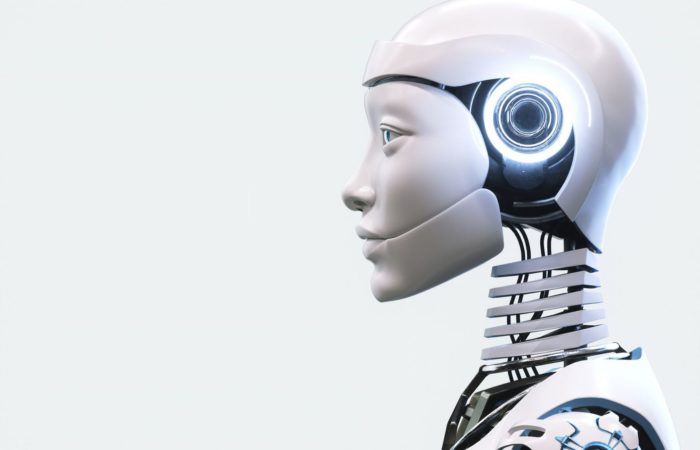
NVIDIA has unveiled a pioneering AI endeavor with the ambition to develop humanoid robots that possess the capacity to learn and undertake intricate tasks through the observation of human behavior. This avant-garde initiative, named GR00T (Generalist Robot 00 Technology), signifies a monumental advancement in the spheres of artificial intelligence and robotics. Additionally, NVIDIA introduced the Jetson Thor computing architecture, meticulously crafted to energize these humanoid automata, in conjunction with augmentations to its Isaac robotics framework. These enhancements include foundational generative AI models and workflow apparatuses. The GR00T initiative aims to endow robots with the faculty to understand natural language and replicate human gestures by watching and assimilating from human activities. Through this cutting-edge strategy, it is anticipated that robots will swiftly gain skills in coordination, dexterity, and a plethora of other competencies crucial for navigating, adapting, and engaging with the tangible world. NVIDIA envisages a future in which humanoid robots are integrated seamlessly into diverse settings, executing an array of functions with alacrity and exactitude. In a keynote exposition, NVIDIA’s founder and CEO, Jensen Huang, exhibited real-world robots employing the GR00T platform to achieve varied tasks. He illustrated how these robots could further refine their skills via digital counterparts in...